LR - Mathematical Reasoning - Previous Year CAT/MBA Questions
The best way to prepare for LR - Mathematical Reasoning is by going through the previous year LR - Mathematical Reasoning CAT questions. Here we bring you all previous year LR - Mathematical Reasoning CAT questions along with detailed solutions.
Click here for previous year questions of other topics.
It would be best if you clear your concepts before you practice previous year LR - Mathematical Reasoning CAT questions.
If Elavalaki raised Rs. 3 crores in 2013, then what is the smallest possible total amount of money (in Rs. crores) that could have been raised by all the companies in 2012?
- (a)
10
- (b)
9
- (c)
12
- (d)
11
Answer: Option D
Text Explanation :
Consider the solution for the first questions of this set.
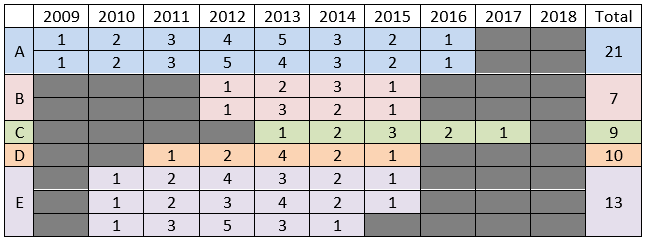
Smallest amount of money that can be raised in 2012 by:
A = 4
B = 1
C = 1
D = 2
E = 3
∴ Smallest total amount of money that can be raised by them in 2012 = 4 + 1 + 1 + 2 + 3 = 11 crores.
Hence, option (d).
Workspace:
If the total amount of money raised in 2014 is Rs. 12 crores, then which of the following is not possible?
- (a)
Alfloo raised the same amount of money as Drjbna in 2013.
- (b)
Bzygoo raised more money than Elavalaki in 2014.
- (c)
Bzygoo raised the same amount of money as Elavalaki in 2013.
- (d)
Alfloo raised the same amount of money as Bzygoo in 2014.
Answer: Option C
Text Explanation :
Consider the solution for the first question of this set.

Amount of money raised in 2014 by
A = 3
B = 2 or 3
C = 2
D = 2
E = 1 or 2
If the total amount of money raised by them in 2014 is 12 crores this is possible only when B raised 3 crores i.e., case 1 for B and E raises 2 crores i.e., case 1 or 2 for E.
We have the following cases left.
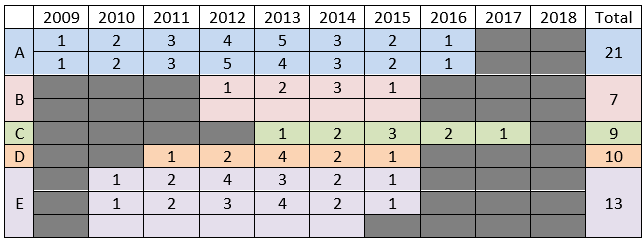
Option (a): A and D can both raise 4 crores in 2013, hence option (a) is possible.
Option (b): B raises 3 crores and E raises 2 crores in 2014, hence option (b) is possible.
Option (c): B cannot raise the same amount as E in 2013, hence option (c) is not possible.
Option (d): A and B can both raise 3 crores in 2014, hence option (d) is possible.
Hence, option (c).
Workspace:
Answer the following questions based on the information given below:
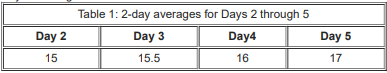
Three participants – Akhil, Bimal and Chatur participate in a random draw competition for five days. Every day, each participant randomly picks up a ball numbered between 1 and 9. The number on the ball determines his score on that day. The total score of a participant is the sum of his scores attained in the five days. The total score of a day is the sum of participants’ scores on that day. The 2-day average on a day, except on Day 1, is the average of the total scores of that day and of the previous day. For example, if the total scores of Day 1 and Day 2 are 25 and 20, then the 2-day average on Day 2 is calculated as 22.5. Table 1 gives the 2-day averages for
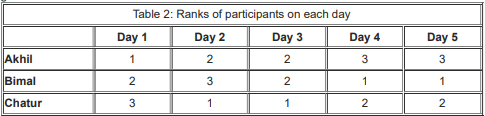
Participants are ranked each day, with the person having the maximum score being awarded the minimum rank (1) on that day. If there is a tie, all participants with the tied score are awarded the best available rank. For example, if on a day Akhil, Bimal, and Chatur score 8, 7 and 7 respectively, then their ranks will be 1, 2 and 2 respectively on that day. These ranks are given in Table 2.
The following information is also known.
- Chatur always scores in multiples of 3. His score on Day 2 is the unique highest score in the competition. His minimum score is observed only on Day 1, and it matches Akhil’s score on Day 4.
- The total score on Day 3 is the same as the total score on Day 4.
- Bimal’s scores are the same on Day 1 and Day 3.
What is Akhil's score on Day 1?
- (a)
7
- (b)
6
- (c)
5
- (d)
8
Answer: Option A
Text Explanation :
We get the following table for their score on each of the 5 days.

Akhil's score on Day 1 is 7.
Hence, option (a).
Workspace:
Who attains the maximum total score?
- (a)
Bimal
- (b)
Chatur
- (c)
Cannot be determined
- (d)
Akhil
Answer: Option B
Text Explanation :
We get the following table for their score on each of the 5 days.

Chatur gets the maximum total score of 30.
Hence, option (b).
Workspace:
What is the minimum possible total score of Bimal?
Answer: 25
Text Explanation :
We get the following table for their score on each of the 5 days.

Minimum total score of Bimal is 25.
Hence, 25.
Workspace:
If Akhil attains a total score of 24, then what is the total score of Bimal?
Answer: 26
Text Explanation :
We get the following table for their score on each of the 5 days.

If Akil gets a total score of 24, Bimal will get a total score of 26.
Hence, 26.
Workspace:
Answer the following questions based on the information given below:
In a coaching class, some students register online, and some others register offline. No student registers both online and offline; hence the total registration number is the sum of online and offline registrations. The following facts and table pertain to these registration numbers for the five months – January to May of 2023. The table shows the minimum, maximum, median registration numbers of these five months, separately for online, offline and total number of registrations. The following additional facts are known.
1. In every month, both online and offline registration numbers were multiples of 10.
2. In January, the number of offline registrations was twice that of online registrations.
3. In April, the number of online registrations was twice that of offline registrations.
4. The number of online registrations in March was the same as the number of offline registrations in February.
5. The number of online registrations was the largest in May.
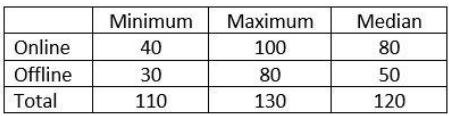
What was the total number of registrations in April?
Answer: 120
Text Explanation :
We get the following table based on the conditions given.
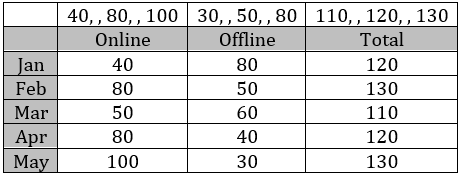
Total registrations in April is 120.
Hence, 120.
Workspace:
What was the number of online registrations in January?
Answer: 40
Text Explanation :
We get the following table based on the conditions given.

Number of online registrations in January is 40.
Hence, 40.
Workspace:
Which of the following statements can be true?
I. The number of offline registrations was the smallest in May.
II. The total number of registrations was the smallest in February.
- (a)
Only II
- (b)
Only I
- (c)
Both I and II
- (d)
Neither I nor II
Answer: Option B
Text Explanation :
We get the following table based on the conditions given.

Offline registrations is smallest in May. Hence, I is correct.
Total registrations was highest in Feb. Hence, II is incorrect.
Hence, option (b).
Workspace:
What best can be concluded about the number of offline registrations in February?
- (a)
50
- (b)
30 or 50 or 80
- (c)
50 or 80
- (d)
80
Answer: Option A
Text Explanation :
We get the following table based on the conditions given.

Number of offline registrations in February is 50.
Hence, option (a).
Workspace:
Which pair of months definitely had the same total number of registrations?
I. January and April
II. February and May
- (a)
Neither I nor II
- (b)
Only II
- (c)
Only I
- (d)
Both I and II
Answer: Option D
Text Explanation :
We get the following table based on the conditions given.

Jan and April both have 120 total registrations.
Feb and May both have 130 total registrations.
Hence, optiono (d).
Workspace:
Answer the following questions based on the information given below:
There are only three female students – Amala, Koli and Rini – and only three male students – Biman, Mathew and Shyamal – in a course. The course has two evaluation components, a project and a test. The aggregate score in the course is a weighted average of the two components, with the weights being positive and adding to 1.
The projects are done in groups of two, with each group consisting of a female and a male student. Both the group members obtain the same score in the project.
The following additional facts are known about the scores in the project and the test.
1. The minimum, maximum and the average of both project and test scores were identical – 40, 80 and 60, respectively.
2. The test scores of the students were all multiples of 10; four of them were distinct and the remaining two were equal to the average test scores.
3. Amala’s score in the project was double that of Koli in the same, but Koli scored 20 more than Amala in the test. Yet Amala had the highest aggregate score.
4. Shyamal scored the second highest in the test. He scored two more than Koli, but two less than Amala in the aggregate.
5. Biman scored the second lowest in the test and the lowest in the aggregate.
6. Mathew scored more than Rini in the project, but less than her in the test.
What was Rini’s score in the project?
Answer: 60
Text Explanation :
We get the following table from conditions given in the question.
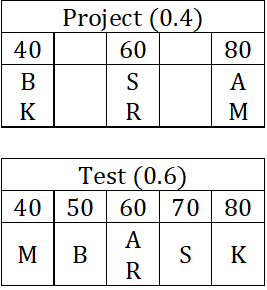
Rani's score in project is 60.
Hence, 60.
Workspace:
What was the weight of the test component?
- (a)
0.75
- (b)
0.60
- (c)
0.40
- (d)
0.50
Answer: Option B
Text Explanation :
We get the following table from conditions given in the question.

Weight of test componenet is 0.6.
Hence, option (b).
Workspace:
What was the maximum aggregate score obtained by the students?
- (a)
66
- (b)
80
- (c)
62
- (d)
68
Answer: Option D
Text Explanation :
We get the following table from conditions given in the question.

Aggregate score was maximum for Amal.
Amala's maximum score = 80 × 0.4 + 60 × 0.6 = 32 + 36 = 68.
Hence, option (d).
Workspace:
What was Mathew’s score in the test?
Answer: 40
Text Explanation :
We get the following table from conditions given in the question.

Mathew's score in test is 40.
Hence, 40.
Workspace:
Which of the following pairs of students were part of the same project team?
i) Amala and Biman
ii) Koli and Mathew
- (a)
Neither i) nor ii)
- (b)
Only ii)
- (c)
Only i)
- (d)
Both i) and ii)
Answer: Option A
Text Explanation :
We get the following table from conditions given in the question.

A and B are not in same team.
K and M are not in same team.
Neither i) nor ii) is correct.
Hence, option (a).
Workspace:
Answer the next 5 questions based on the information given below:
Adhara, Bithi, Chhaya, Dhanavi, Esther, and Fathima are the interviewers in a process that awards funding for new initiatives. Every interviewer individually interviews each of the candidates individually and awards a token only if she recommends funding. A token has a face value of 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, or 13. Each interviewer awards tokens of a single face value only.
Once all six interviews are over for a candidate, the candidate receives a funding that is Rs.1000 times the product of the face values of all the tokens. For example, if a candidate has tokens with face values 2, 5, and 7, then they get a funding of Rs.1000 × (2 × 5 × 7) = Rs.70,000.
Pragnyaa, Qahira, Rasheeda, Smera, and Tantra were five candidates who received funding. The funds they received, in descending order, were Rs.390,000, Rs.210,000, Rs.165,000, Rs.77,000, and Rs.66,000.
The following additional facts are known:
1. Fathima awarded tokens to everyone except Qahira, while Adhara awarded tokens to no one except Pragnyaa.
2. Rashida received the highest number of tokens that anyone received, but she did not receive one from Esther.
3. Bithi awarded a token to Smera but not to Qahira, while Dhanavi awarded a token to Qahira but not to Smera.
How many tokens did Qahira receive?
Answer: 2
Text Explanation :
The funds they received, in descending order, were Rs.390,000, Rs.210,000, Rs.165,000, Rs.77,000, and Rs.66,000.
∴ The product of tokes = 390, 210, 165, 77, 66
⇒ Break of tokens received
390 = 2 × 3 × 5 × 13
210 = 2 × 3 × 5 × 7
165 = 3 × 5 × 11
77 = 7 × 11
66 = 2 × 3 × 11
From (1): Fathima awarded tokens to everyone except Qahira,
∴ Fatima must have awarded token number 3 to everyone and Qahira received tokens whose product is 77.
From (1): Adhara awarded tokens to no one except Pragnyaa
∴ Adhara must have awared token 13 and Pragnyaa received tokens whose product is 390.

From (2): Rashida received the highest number of tokens that anyone received, but she did not receive one from Esther.
∴ Rashida must have received 4 tokes whose product can only be 210. Also, since Esther did not give her the token, hence Esther must have distributed token number 11.

From (3): Dhanavi awarded a token to Qahira but not to Smera.
∴ Dhanavi must have awared token number 7.

From (3): Bithi awarded a token to Smera but not to Qahira
∴ Bithi/Chhaya could have awared token 2/5 in any order.

If Bithi gives token number 2 to S/T, then Chhaya will given token number 5 to T/S and vice-a-versa.
∴ Qahira received two tokens i.e., 7 and 11.
Hence, 2.
Workspace:
Who among the following definitely received a token from Bithi but not from Dhanavi?
- (a)
Qahira
- (b)
Tantra
- (c)
Rasheeda
- (d)
Pragnyaa
Answer: Option D
Text Explanation :
Consider the solution to first question of this set.
In any of the cases, Pragnyaa definitely received a token from Bithi but not from Dhanavi
Hence, option (d).
Workspace:
How many tokens did Chhaya award?
Answer: 3
Text Explanation :
Consider the solution to first question of this set.
In any of the cases, Chhaya will definitely distribute 3 tokens.
i.e., to (Pragnyaa, Rasheeda and Smera) or to (Pragnyaa, Rasheeda and Tantra)
Hence, 3.
Workspace:
How many tokens did Smera receive?
Answer: 3
Text Explanation :
Consider the solution to first question of this set.
In any of the cases, Smera will definitely receive 3 tokens.
i.e., (2, 3 and 11) or (3, 5 and 11)
Hence, 3.
Workspace:
Which of the following could be the amount of funding that Tantra received?
(a) Rs. 66,000
(b) Rs. 165,000
- (a)
Neither (a) nor (b)
- (b)
Both (a) and (b)
- (c)
Only (b)
- (d)
Only (a)
Answer: Option B
Text Explanation :
Consider the solution to first question of this set.
Tanta could receive either (2, 3 and 11) tokes or (3, 5 and 11) tokes
i.e., Tanta’s funds can either be Rs. 66,000 or Rs. 165,000
Hence, option (b).
Workspace:
Answer the next 4 questions based on the information given
Each of the bottles mentioned in this question contains 50 ml of liquid. The liquid in any bottle can be 100% pure content (P) or can have certain amount of impurity (I). Visually it is not possible to distinguish between P and I. There is a testing device which detects impurity, as long as the percentage of impurity in the content tested is 10% or more.
For example, suppose bottle 1 contains only P, and bottle 2 contains 80% P and 20% I. If content from bottle 1 is tested, it will be found out that it contains only P. If content of bottle 2 is tested, the test will reveal that it contains some amount of I. If 10 ml of content from bottle 1 is mixed with 20 ml content from bottle 2, the test will show that the mixture has impurity, and hence we can conclude that at least one of the two bottles has I. However, if 10 ml of content from bottle 1 is mixed with 5 ml of content from bottle 2. the test will not detect any impurity in the resultant mixture.
5 ml of content from bottle A is mixed with 5 ml of content from bottle B. The resultant mixture, when tested, detects the presence of I. If it is known that bottle A contains only P, what BEST can be concluded about the volume of I in bottle B?
- (a)
10 ml or more
- (b)
Less than 1 ml
- (c)
10 ml
- (d)
1 ml
Answer: Option A
Text Explanation :
Since impurity is detected in the final mixture, hence the mixture has at least 10% impurities.
∴ % impurity in the mixture = ≥ 10
⇒ 5P ≥ 100
⇒ P ≥ 20%
∴ Volume of impurities in bottle B is at least 20% of 50 ml i.e., ≥ 10 ml.
Hence, option (a).
Workspace:
There are four bottles. Each bottle is known to contain only P or only I. They will be considered to be “collectively ready for despatch” if all of them contain only P. In minimum how many tests, is it possible to ascertain whether these four bottles are “collectively ready for despatch”?
Answer: 1
Text Explanation :
The bottles contain only P or only I.
Let us mix equal quantities from each of these bottles and check for impurities.
Case 1: All bottles contain only P
Concentration of I in final mixture = = 0%
∴ Impurities will not be detected.
Case 2: 3 bottles contain P and 1 contains I
Concentration of I in final mixture = = 25%
∴ Impurities will be detected.
Case 3: 2 bottles contain P and 2 contain I
Concentration of I in final mixture = = 50%
∴ Impurities will be detected.
Case 4: 1 bottle contains P and 3 contain I
Concentration of I in final mixture = = 75%
∴ Impurities will be detected.
Case 5: All bottles contain only I
Concentration of I in final mixture = = 100%
∴ Impurities will be detected.
There is only one case where impurities are not detected and that is when all the bottles have only P.
⇒ If we mix equal quantities of all 4 bottles and test for impurities, if impurity is not detected then we can safely accept all 4 bottles.
Only one test is required is such a situation.
Hence, 1.
Workspace:
There are four bottles. It is known that three of these bottles contain only P, while the remaining one contains 80% P and 20% I. What is the minimum number of tests required to definitely identify the bottle containing some amount of I?
Answer: 2
Text Explanation :
Let the bottles be A, B, C and D.
We first mix equal quantities of A and B and test the mixture.
Case 1: If any one of A or B contains 20% impurities, test will detect the impurity.
Then we check A for impurity. If impurity is detected then A contains I else B contains I.
∴ 2 tests are required to detect I.
Case 2: If none of A or B contains impurities, test will not detect the impurity.
This means one of C or D contains I.
Then we check C for impurity. If impurity is detected then C contains I else D contains I.
∴ 2 tests are required to detect I.
In both cases 2 tests are required to detect I.
Hence, 2.
Workspace:
There are four bottles. It is known that either one or two of these bottles contain(s) only P, while the remaining ones contain 85% P and 15% I. What is the minimum number of tests required to ascertain the exact number of bottles containing only P?
- (a)
3
- (b)
2
- (c)
4
- (d)
1
Answer: Option D
Text Explanation :
Case 1: Only bottle contains pure P.
Now if we mix equal quantities from each of the 4 bottles, the concentration of I in the mixture = = 11.25%
∴ Testing this mixture will detect the impurities.
Case 2: 2 bottles contains pure P.
Now if we mix equal quantities from each of the 4 bottles, the concentration of I in the mixture = = 7.5%
∴ Testing this mixture will not detect the impurities.
⇒ Mix equal quantities of all 4 bottles, it I is detected then only 1 bottle contains P else 2 bottles contain P.
Hence, option (d).
Workspace:
 Solution
Solution Discuss
Discuss Report
Report